Developing for Sailfish OS: working with LocalStorage
Hello! This article is a continuation of the series of articles dedicated to developing for the mobile platform Sailfish OS. This time we decided to talk about the control of Finance, allowing the user to log income and expenses and set aside funds to achieve its goals. It is worth mentioning that this application is one of the winners of the hackathon on Sailfish OS in Yaroslavl organized by the company "Open Mobile Platform" and the Association FRUCT.
Our application includes two separate modules. The first of these is designed to work directly with the operations. The second allows the user to create goals and track the progress of accumulation.
Module for working with the operations allows the user to record income and expenses, and show these transactions in the form of a journal:
the
As you can see from the screenshot add, for each operation defined category. This classification helps the user to navigate easier in your finances. In addition to the standard categories, the user can add their own, thereby adjusting the application to fit your lifestyle.
In addition, the application provides the ability to view statistics for various periods of time to allow the user to analyze their spending in the future to optimize them:
the
The second module of the application provides the ability to create tasks for the accumulation of funds for any purpose. The user can record in the application information about how much he is saving funds for a particular purpose,
and track progress, thereby motivating yourself in performing your tasks:
the
In this article, we decided to focus on working with the database directly from QML files. For realization of this task was used the library LocalStorage, allowing to organize access to SQLite databases stored on the device.
For separation logic work with the database of items was created QML object for data access (data access object, or simply DAO) that manages all the connections with the base and providing a more convenient interface for working with data. The database connection can be opened using the global singleton object LocalStorage. It is called the method openDatabaseSync(), which directly opens a connection or creates the database if it has not been created earlier. All connections are automatically closed when garbage collected. The following is part of the code of the Dao file.qml:
the
Transactions and queries when the database is designed as a function JS: for
the results of the required callback function invoked at the end of operations. The resulting connection object to invoke methods of readTransaction() and transaction(), which create a transaction to read or modify the data, and pass it the callback function specified as argument of these methods. Inside of these functions can be called by methods of executeSql() that contains SQL queries.
In our application we had to create a database with three tables: TransactionsTable storage operations GoalTable goals and CategoriesTable to categories of operations:
the
It is worth mentioning that the operations on creation of database and its initialization must be placed inside a signal handler Component.onCompleted to perform when creating the Dao object.
A method that adds a new record in the operations table looks like the following:
the
A method that retrieves the list of targets will look like the following:
the
Here are the result of executeSql() is an object that contains the property rows with a list of all result records. To obtain the i-th element, it is sufficient to call the method rows.item(i). The number of items available on the property rows.length. An example of the use of the method described:
the
This code shows that the values of the record fields of the database available as properties of the object var goal = goals.item(i). Given this, a query with a calculated field will look like:
the
Also in our app added filtering records by date. As you know, SQLite has no standard types for working with dates. Instead, SQLite supports five functions for working with date and time. All dates in the database we store a string in the ISO8601 format. Example query to retrieve the earliest date of operation as follows:
the
On the QML side when working with dates use the QML class Date inherited from class Date from Javascript. To continue with the result of the query must be run:
the
To convert the object back to a string in the ISO8601 format, you must use the toISOString().
the
As a result, was created an application that allows you to store information about the finances of the user. The app was published in app store, Jolla Harbour called Save Your money and available for download to everyone. The source code of the application available on Bitbucket.
Technical questions can be discussed on channel Russian-speaking community of Sailfish OS in Telegram or Facebook page.
Author: Daria Raichinov
Article based on information from habrahabr.ru
Description
Our application includes two separate modules. The first of these is designed to work directly with the operations. The second allows the user to create goals and track the progress of accumulation.
Module for working with the operations allows the user to record income and expenses, and show these transactions in the form of a journal:
 |
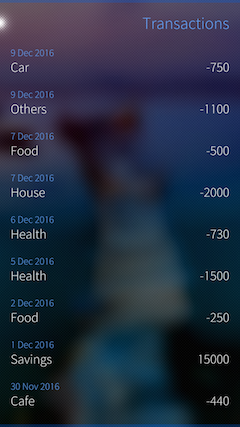 |
As you can see from the screenshot add, for each operation defined category. This classification helps the user to navigate easier in your finances. In addition to the standard categories, the user can add their own, thereby adjusting the application to fit your lifestyle.
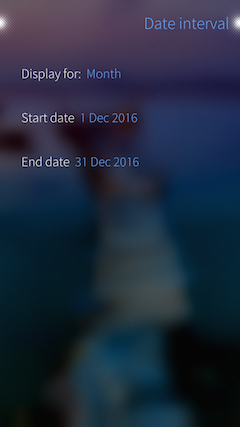
In addition, the application provides the ability to view statistics for various periods of time to allow the user to analyze their spending in the future to optimize them:
 |
 |
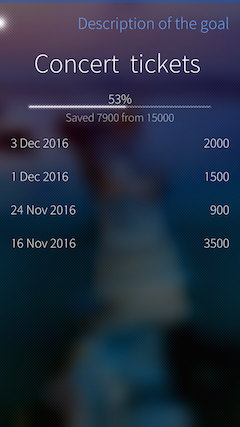
The second module of the application provides the ability to create tasks for the accumulation of funds for any purpose. The user can record in the application information about how much he is saving funds for a particular purpose,
and track progress, thereby motivating yourself in performing your tasks:

the
the database
In this article, we decided to focus on working with the database directly from QML files. For realization of this task was used the library LocalStorage, allowing to organize access to SQLite databases stored on the device.
For separation logic work with the database of items was created QML object for data access (data access object, or simply DAO) that manages all the connections with the base and providing a more convenient interface for working with data. The database connection can be opened using the global singleton object LocalStorage. It is called the method openDatabaseSync(), which directly opens a connection or creates the database if it has not been created earlier. All connections are automatically closed when garbage collected. The following is part of the code of the Dao file.qml:
the
import QtQuick 2.0
import QtQuick.LocalStorage 2.0
Item {
Component.onCompleted: {
database = LocalStorage.openDatabaseSync("SaveYourMoneyDatabase", "1.0")
}
//...
}
Transactions and queries when the database is designed as a function JS: for
the results of the required callback function invoked at the end of operations. The resulting connection object to invoke methods of readTransaction() and transaction(), which create a transaction to read or modify the data, and pass it the callback function specified as argument of these methods. Inside of these functions can be called by methods of executeSql() that contains SQL queries.
In our application we had to create a database with three tables: TransactionsTable storage operations GoalTable goals and CategoriesTable to categories of operations:
the
Component.onCompleted: {
database = LocalStorage.openDatabaseSync("SaveYourMoneyDatabase", "1.0")
tx.executeSql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS TransactionsTable(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
date TEXT
sum INTEGER,
category_id INTEGER,
type INTEGER,
goal_id INTEGER,
description TEXT)");
tx.executeSql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS CategoriesTable(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT,
type INTEGER)");
tx.executeSql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS GoalTable(
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT,
sum INTEGER,
isFinished INTEGER)");
// ...
}
});
}
It is worth mentioning that the operations on creation of database and its initialization must be placed inside a signal handler Component.onCompleted to perform when creating the Dao object.
A method that adds a new record in the operations table looks like the following:
the
function createTransaction(date, sum, category_id, type, description) {
database.transaction(function(tx) {
tx.executeSql("INSERT INTO TransactionsTable(date, sum, category_id, type, description) VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)", [date, sum, category_id, type, description]);
});
}
A method that retrieves the list of targets will look like the following:
the
function retrieveGoals(isFinished, callback) {
database = LocalStorage.openDatabaseSync("SaveYourMoneyDatabase", "1.0");
database.readTransaction(function(tx) {
var result = tx.executeSql("SELECT * FROM GoalTable WHERE isFinished = ? ORDER BY id ASC", [isFinished]);
callback(result.rows)
});
}
Here are the result of executeSql() is an object that contains the property rows with a list of all result records. To obtain the i-th element, it is sufficient to call the method rows.item(i). The number of items available on the property rows.length. An example of the use of the method described:
the
Dao { id: dao }
SilicaListView {
id: listView
model: GoalListModel { id: goalsListModel }
delegate: ListItem {
// ...
}
// ...
}
displayGoals function() {
listView.model.clear();
dao.retrieveGoals(true, function(goals) {
for (var i = 0; i < goals.length; i++) {
var goal = goals.item(i);
listView.model.addGoal(goal.id, goal.name, goal.sum);
}
});
}
Component.onCompleted: displayGoals();
This code shows that the values of the record fields of the database available as properties of the object var goal = goals.item(i). Given this, a query with a calculated field will look like:
the
function retrieveGoalStatistics(callback) {
database = LocalStorage.openDatabaseSync("SaveYourMoneyDatabase", "1.0");
database.readTransaction(function(tx) {
var result = tx.executeSql("SELECT SUM(SUM) AS goalSum FROM GoalTable WHERE isFinished = 0");
callback(result.rows.item(0).goalSum)
});
}
Also in our app added filtering records by date. As you know, SQLite has no standard types for working with dates. Instead, SQLite supports five functions for working with date and time. All dates in the database we store a string in the ISO8601 format. Example query to retrieve the earliest date of operation as follows:
the
function retrieveDateOfFirstTransaction(callback) {
database = LocalStorage.openDatabaseSync("SaveYourMoneyDatabase", "1.0");
database.readTransaction(function(tx) {
var result = tx.executeSql("SELECT MIN(date(date)) as minDate FROM TransactionsTable");
callback(result.rows.item(0).minDate)
});
}
On the QML side when working with dates use the QML class Date inherited from class Date from Javascript. To continue with the result of the query must be run:
the
dao.retrieveDateOfFirstTransaction(function(result){
startDate = new Date(result);
});
To convert the object back to a string in the ISO8601 format, you must use the toISOString().
the
Conclusion
As a result, was created an application that allows you to store information about the finances of the user. The app was published in app store, Jolla Harbour called Save Your money and available for download to everyone. The source code of the application available on Bitbucket.
Technical questions can be discussed on channel Russian-speaking community of Sailfish OS in Telegram or Facebook page.
Author: Daria Raichinov
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий