Publish logs in Elasticsearch — life without regular expressions, and without logstash
If you use the approach from this solution, the parsing of the files would not be necessary. If you change the logging format or new messages do not need to support a large set of regexps. Will intercept calls to methods error, warn, info, debug, trace logger and send the data directly to elasticsearch. This will help us to aspect-oriented programming!
Screencast you can watch to the end.
Hope you will be interested to learn how to use aspects written in the form of a script and configuration to work with elasticsearch client, gson serializer and the parameters of the intercepted method in the jvm.
The experimental program remains SonarQube, as in articles about hawt.io/h2, jdbc logging and CRaSH-ssh. Read more about the process of installing and configuring sonar and agent virtual machines you can read in the publication about hawt.io/h2.
This time will use the jvm startup options sonar:
sonar.web.javaAdditionalOpts=-javaagent:aspectj-scripting-1.0-agent.jar -Dorg.aspectj.weaver.loadtime.configuration=config:file:es.xml
And for the sample you need to download a jvm agent aspectj-scripting and the configuration file es.xml:
the
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<configuration>
<aspects>
<name>com.github.igorsuhorukov.Loging</name>
<type>AROUND</type>
<pointcut>call(* org.slf4j.Logger.error(..)) || call(* org.slf4j.Logger.warn(..)) || call(* org.slf4j.Logger.info(..)) || call(* org.slf4j.Logger.debug(..)) || call(* org.slf4j.Logger.trace(..))</pointcut>
<process>
<expression>
res = joinPoint.proceed();
log = new java.util.HashMap();
log.put("level", joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
log.put("srcf", joinPoint.getSourceLocation().getFileName().substring(0, joinPoint.getSourceLocation().getFileName().length()-5));
log.put("srcl", joinPoint.getSourceLocation().getLine());
if(joinPoint.getArgs()!=null && joinPoint.getArgs().?length>0){
log.put("message", joinPoint.getArgs()[0].?toString());
if(joinPoint.getArgs().length > 1){
params = new java.util.HashMap();
for(i=1; i < joinPoint.getArgs().length;i++){
if(joinPoint.getArgs()[i]!=null){
if(joinPoint.getArgs()[i].class.getName().equals("[Ljava.lang.Object;")){
for(j=0; j < joinPoint.getArgs()[i].length;j++){
if( (joinPoint.getArgs()[i])[j] !=null){
params.put(i+"."+j,(joinPoint.getArgs()[i])[j].toString());
}
}
} else {
params.put(i,joinPoint.getArgs()[i].toString());
}
}
}
log.put("params", params);
}
}
log.put("host", reportHost); log.put("pid", pid);
log.put("@version", 1);
localDate = new java.util.Date();
lock.lock();
log.put("@timestamp", dateFormat.format(localDate));
index = "logstash" + logstashFormat.format(localDate);
lock.unlock();
logSource = gson.toJson(log);
client.index(client.prepareIndex(index, "logs").setSource(logSource).request());
res;
</expression></process>
</aspects>
<access>
<artifacts>
<artifact>com.google.code.gson:gson:2.3.1</artifact>
<classRefs>
<variable>GsonBuilder</variable>
<className>com.google.gson.GsonBuilder</className>
</classRefs>
</artifacts>
<artifacts>
<artifact>org.elasticsearch:elasticsearch:1.1.1</artifact>
<classRefs>
<variable>NodeBuilder</variable>
<className>org.elasticsearch.node.NodeBuilder</className>
</classRefs>
</artifacts>
<init>
<expression>
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.TimeZone;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
reportHost = java.net.InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostName();
pid = java.lang.management.ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getName().split("@")[0];
gson = new GsonBuilder().create();
dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-DD't'hh:mm:ss.SSS'Z'");
dateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
logstashFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd");
logstashFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
lock = new ReentrantLock();
client = NodeBuilder.nodeBuilder().clusterName("distributed_app").data(false).client(true).build().client();
</expression>
</init>
</access>
</configuration>
For all call points from the program methods error, warn, info, debug, trace, interface org.slf4j.Logger, called the aspect in which we create a HashMap and fill in the log settings call context: class file "srcf" and this "srcl", specify the logging level level, host name "host", process ID "pid", the logger "@timestamp", and the template text of the message and separately in Map "params" saved settings. All of this synchronously with the invocation is serialized to json and sent to the index with the name "logstash" + the call date. The classes for formatting date and time, as well as the client for elasticsearch is created when the application is launched in block of the global initialization aspects globalContext.
The client from the aspect when you start using multicast Protocol tries to find the elasticsearch cluster with the name "distributed_app"
Before starting our client be sure to run a cluster of elasticsearch servers consisting of a single process:
the
package org.github.suhorukov;
import org.elasticsearch.common.settings.ImmutableSettings;
import org.elasticsearch.node.Node;
import org.elasticsearch.node.NodeBuilder;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ElasticsearchServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String template;
try(InputStream templateStream = new URL("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/logstash-plugins/logstash-output-elasticsearch/master/lib/logstash/outputs/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-template.json").openStream()){
template = new String(sun.misc.IOUtils.readFully(templateStream, -1, true));
}
Node elasticsearchServer = NodeBuilder.nodeBuilder().settings(ImmutableSettings.settingsBuilder().put("http.cors.enabled","true")).clusterName("distributed_app").data(true).build();
Node node = elasticsearchServer.start();
node.client().admin().indices().preparePutTemplate("logstash").setSource(template).get();
Thread.sleep(TimeUnit.HOURS.toMillis(5));
}
}
To compile and work this class required dependency:
the
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
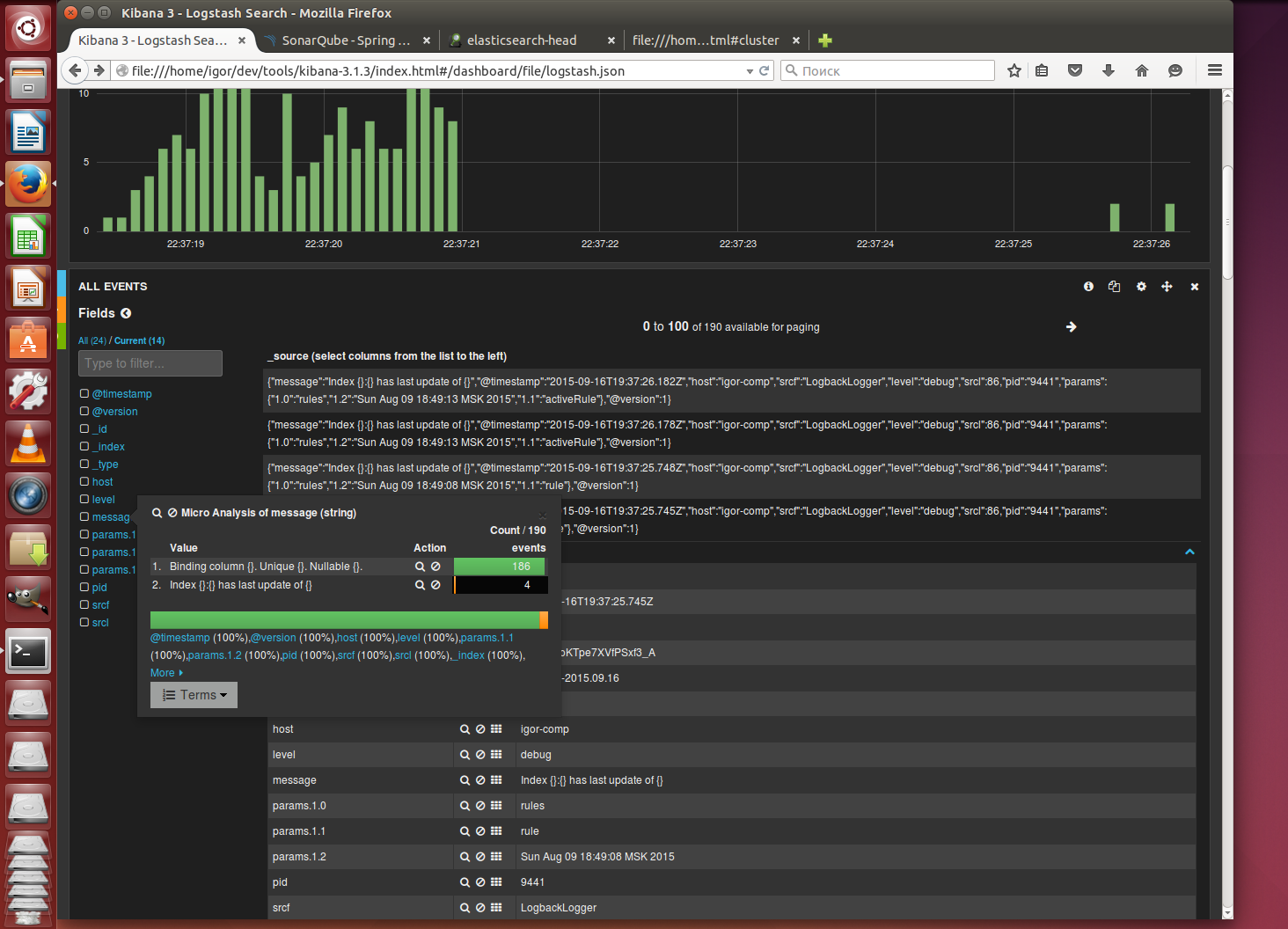
To view log download the old build kibana 3.1.3 that can work without a web server. Edit the file config.js the
elasticsearch: "http://127.0.0.1:9200"Run sonar
the
./bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh startsee in the browser as in the process of SonarQube in kibana shows the events of this system
What about the examples using aspects you would like to read? Offer!
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий